SCIENCE

The surprising brain chemistry behind instant friendships
- By Neclink.com
- . August 14, 2025
A new UC Berkeley study shows that the so-called love hormone, oxytocin, is also critical for the formation of friendships. Oxytocin is released in the

The hidden mental health danger in today’s high-THC cannabis
- By Neclink.com
- . August 13, 2025
Science News from research organizations Date: August 12, 2025 Source: Canadian Medical Association Journal Summary: THC levels in cannabis have soared in recent years, raising

What scientists discovered about french fries and diabetes
- By Neclink.com
- . August 12, 2025
Eating three servings of French fries a week is associated with a 20% increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, but eating similar amounts of

This tiny spacecraft could race to a black hole and rewrite physics
- By Neclink.com
- . August 11, 2025
It sounds like science fiction: a spacecraft, no heavier than a paperclip, propelled by a laser beam and hurtling through space at the speed of

Scientists find brain cell switch that could reverse obesity’s effects
- By Neclink.com
- . August 10, 2025
Researchers show astrocytes can be tuned to reverse some obesity-driven brain and metabolic changes, revealing untapped therapeutic potential. Credit: Shutterstock Fatty diets and obesity affect

Scientists reveal Alaska could get up to two minutes’ warning before the next big quake
- By Neclink.com
- . August 9, 2025
For a wide variety of earthquake scenarios in Alaska, an earthquake early warning (EEW) system could provide at least 10 seconds of warning time for

Hubble just exposed a rare and violent star collision
- By Neclink.com
- . August 8, 2025
University of Warwick astronomers have uncovered compelling evidence that a nearby white dwarf is in fact the remnant of two stars merging — a rare
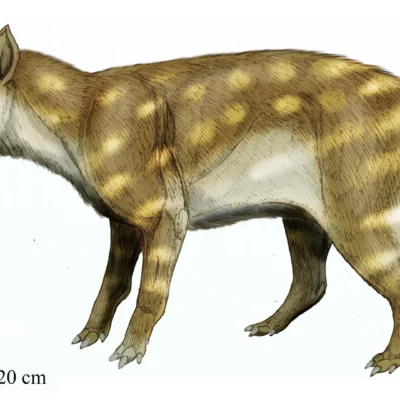
This prehistoric predator survived global warming by eating bones
- By Neclink.com
- . August 7, 2025
About 56 million years ago, when Earth experienced a dramatic rise in global temperatures, one meat-eating mammal responded in a surprising way: It started eating

This diet helped people lose twice as much weight, without eating less
- By Neclink.com
- . August 6, 2025
When given nutritionally matched diets, participants lost twice as much weight eating minimally processed foods compared to ultra-processed foods, suggesting that cutting down on processing

Scientists reexamine 47-year-old fossil and discover a new Jurassic sea monster
- By Neclink.com
- . August 5, 2025
Paleontologists have identified a new species of ancient marine reptile from Germany’s world-renowned Posidonia Shale fossil beds, expanding our understanding of prehistoric ocean ecosystems that
